चित्र:Navier Stokes Laminar.svg
testwiki से
नेविगेशन पर जाएँ
खोज पर जाएँ

पूर्वावलोकन PNG का आकार SVG फ़ाइल: ७५० × ६०० पिक्सेल दूसरे रेसोल्यूशन्स: ३०० × २४० पिक्सेल | ६०० × ४८० पिक्सेल | ९६० × ७६८ पिक्सेल | १,२८० × १,०२४ पिक्सेल | २,५६० × २,०४८ पिक्सेल | ९०० × ७२० पिक्सेल।
मूल चित्र (SVG फ़ाइल, साधारणतः ९०० × ७२० पिक्सेल, फ़ाइल का आकार: ९.३७ MB)
यह चित्र विकिमीडिया कॉमन्स से है और दूसरे परियोजनाओं द्वारा भी प्रयोग की जा सकती है। वहाँ पर इसके चित्र विवरण पृष्ठ में मौजूद विवरण नीचे दिखाई गई है।
सारांश
| विवरणNavier Stokes Laminar.svg |
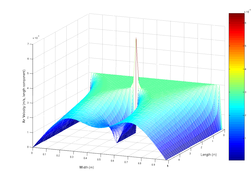
English: SVG illustration of the classic Navier-Stokes obstructed duct problem, which is stated as follows. There is air flowing in the 2-dimensional rectangular duct. In the middle of the duct, there is a point obstructing the flow. We may leverage Navier-Stokes equation to simulate the air velocity at each point within the duct. This plot gives the air velocity component of the direction along the duct. One may refer to [1], in which Eq. (3) is a little simplified version compared with ours. |
| दिनांक | |
| स्रोत |
अपना कार्य
The following code leverages some numerical methods to simulate the solution of the 2-dimensional Navier-Stokes equation. We choose the simplified incompressible flow Navier-Stokes Equation as follows: The iterations here are based on the velocity change rate, which is given by Or in X coordinates: |
| लेखक | IkamusumeFan |
| दूसरे संस्करण |
  |
| SVG genesis InfoField | इस वेक्टर चित्र को Matplotlib की मदद से बनाया गया था। |
| मूल कोड InfoField | Python codefrom __future__ import division
from numpy import arange, meshgrid, sqrt, zeros, sum
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.ticker import ScalarFormatter
from matplotlib import rcParams
rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'
rcParams['font.size'] = 16
# the layout of the duct laminar
x_max = 5 # duct length
y_max = 1 # duct width
# draw the frames, including the angles and labels
ax = Axes3D(plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)), azim=20, elev=20)
ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$", fontsize=20)
ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$", fontsize=20)
ax.zaxis.set_rotate_label(False)
ax.set_zlabel(r"$v_x$", fontsize=20, rotation='horizontal')
formatter = ScalarFormatter(useMathText=True)
formatter = ScalarFormatter()
formatter.set_scientific(True)
formatter.set_powerlimits((-2,2))
ax.w_zaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
ax.set_xlim([0, x_max])
ax.set_ylim([0, y_max])
# initial speed of the air
ini_v = 3e-3
mu = 1e-5
rho = 1.3
# the acceptable difference when termination
accept_diff = 1e-5
# time interval
time_delta = 1.0
# coordinate interval
delta = 1e-2;
X = arange(0, x_max + delta, delta)
Y = arange(0, y_max + delta, delta)
# number of coordinate points
x_size = len(X) - 1
y_size = len(Y) - 1
Vx = zeros((len(X), len(Y)))
Vy = zeros((len(X), len(Y)))
new_Vx = zeros((len(X), len(Y)))
new_Vy = zeros((len(X), len(Y)))
# initial conditions
Vx[1: x_size - 1, 2:y_size - 1] = ini_v
# start evolution and computation
res = 1 + accept_diff
rounds = 0
alpha = mu/(rho * delta**2)
while (res>accept_diff and rounds<100):
"""
The iterations here are based on the velocity change rate, which
is given by
\frac{\partial v}{\partial t} = \alpha\nabla^2 v - v \cdot \nabla v
with \alpha = \mu/\rho.
"""
new_Vx[2:-2, 2:-2] = Vx[2:-2, 2:-2] + time_delta*(alpha*(Vx[3:-1, 2:-2] +
Vx[2:-2, 3:-1] - 4*Vx[2:-2, 2:-2] + Vx[2:-2, 1:-3] + Vx[1:-3, 2:-2]) -
0.5/delta * (Vx[2:-2, 2:-2] * (Vx[3:-1, 2:-2] - Vx[1:-3, 2:-2]) +
Vy[2:-2, 2:-2]*(Vx[2:-2, 3:-1] - Vx[2:-2, 1:-3])))
new_Vy[2:-2, 2:-2] = Vy[2:-2, 2:-2] + time_delta*(alpha*(Vy[3:-1, 2:-2] +
Vy[2:-2, 3:-1] - 4*Vy[2:-2, 2:-2] + Vy[2:-2, 1:-3] + Vy[1:-3, 2:-2]) -
0.5/delta * (Vy[2:-2, 2:-2] * (Vy[2:-2, 3:-1] - Vy[2:-2, 3:-1]) +
Vx[2:-2, 2:-2]*(Vy[3:-1, 2:-2] - Vy[1:-3, 2:-2])))
rounds = rounds + 1
# copy the new values
Vx[2:-2, 2:-2] = new_Vx[2:-2, 2:-2]
Vy[2:-2, 2:-2] = new_Vy[2:-2, 2:-2]
# set free boundary conditions: dv_x/dx = dv_y/dx = 0.
Vx[-1, 1:-1] = Vx[-3, 1:-1]
Vx[-2, 1:-1] = Vx[-3, 1:-1]
Vy[-1, 1:-1] = Vy[-3, 1:-1]
Vy[-2, 1:-1] = Vy[-3, 1:-1]
# there exists a still object in the plane
Vx[x_size//3:x_size//1.5, y_size//2.0] = 0
Vy[x_size//3:x_size//1.5, y_size//2.0] = 0
# calculate the residual of Vx
res = (Vx[3:-1, 2:-2] + Vx[2:-2, 3:-1] -
Vx[1:-3, 2:-2] - Vx[2:-2, 1:-3])**2
res = sum(res)/(4 * delta**2 * x_size * y_size)
# prepare the plot data
Z = sqrt(Vx**2)
# refine the region boundary
Z[0, 1:-2] = Z[1, 1:-2]
Z[-2, 1:-2] = Z[-3, 1:-2]
Z[-1, 1:-2] = Z[-3, 1:-2]
Y, X = meshgrid(Y, X);
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap="summer", lw=0.1,
edgecolors="k")
plt.savefig("Navier_Stokes_Laminar.svg")
|
लाइसेंस
मैं, इस कार्य का/की कॉपीराइट धारक, इसे निम्न लाइसेंस के अंतर्गत प्रकाशित करता/करती हूँ:
इस फ़ाइल को क्रिएटिव कॉमन्स श्रेय-समानसांझा 4.0 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय लाइसेंस के अंतर्गत लाइसेंस किया गया है।
- आप खुलकर:
- बाँट सकते हैं – रचना की प्रतिलिपि बना सकते हैं, बाँँट सकते हैं और संचारित कर सकते हैं
- रीमिक्स कर सकते हैं – कार्य को अनुकूलित कर सकते हैं
- निम्नलिखित शर्तों के अंतर्गत:
- श्रेय – यह अनिवार्य है कि आप यथोचित श्रेय प्रदान करें, लाइसेंस की कड़ी प्रदान करें, और अगर कोई बदलाव हुए हों तो उन्हें इंगित करें। आप ऐसा किसी भी उचित तरीके से कर सकते हैं, लेकिन किसी भी तरह उससे यह नहीं संकेत नहीं किया जाना चाहिए कि लाइसेंसधारी द्वारा आपको अथवा आपके इस प्रयोग का समर्थन किया जा रहा हो।
- समानसांझा – अगर आप इस रचना में कोई बदलाव करते हैं या इसपर आधारित कुछ रचित करते हैं तो आप अपने योगदान को सिर्फ इसी या इसके सामान किसी लाइसेंस के अंतर्गत बाँट सकते हैं।
- ↑ Fan, Chien, and Bei-Tse Chao. "Unsteady, laminar, incompressible flow through rectangular ducts." Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP 16, no. 3 (1965): 351-360.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
project
Items portrayed in this file
चित्रण
source of file अंग्रेज़ी
original creation by uploader अंग्रेज़ी
चित्र का इतिहास
चित्र पुराने समय में कैसी दिखती थी यह जानने के लिए दिनांक/समय पर क्लिक करें।
| दिनांक/समय | थंबनेल | आकार | सदस्य | टिप्पणी | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| वर्तमान | ०२:०६, १५ मार्च २०१६ |  | ९०० × ७२० (९.३७ MB) | wikimediacommons>Nicoguaro | Smaller version |
चित्र का उपयोग
यह पृष्ठ इस चित्र का इस्तेमाल करता है:


